Hazelbaker Assessment Tool for Lingual Frenulum Function
The following is an exerpt from Ankyloglossia: Assessment,Incidence, and Effect of Frenuloplasty on the Breastfeeding Dyad
Jeanne L. Ballard, Christine E. Auer and Jane C. Khoury
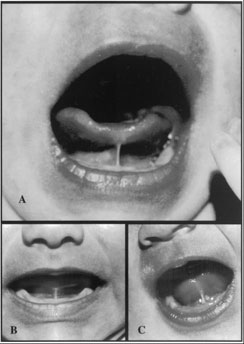
The Hazelbaker score was calculated after scoring the appearance and function items using the following method: The appearance of the tongue when lifted is determined by inspecting the anterior edge of the tongue as the infant cries or tries to lift or extend the tongue. The elasticity of the frenulum is determined by palpating the frenulum for elasticity while lifting the infant?s tongue. The length of the lingual frenulum is determined by noting its approximate length in centimeters as the tongue is lifted. Attachment of the frenulum to the tongue is determined by noting its origin on the inferior aspect of the tongue. It should be approximately 1 cm posterior to the tip. The attachment of the lingual frenulum to the inferior alveolar ridge is determined by noting the location of the anterior attachment of the frenulum. It should insert proximal to or into the genioglossus muscle on the floor of the mouth.
Assessment and Interpretation of Lingual Characteristics
Lateralization is measured by eliciting the transverse tongue reflex by tracing the lower gum ridge and brushing the lateral edge of the tongue with the examiner's finger. Lift of the tongue is noted when the finger is removed from the infant's mouth. If the infant cries, then the tongue tip should lift to mid-mouth without jaw closure. Extension of the tongue is measured by eliciting the tongue extrusion reflex by brushing the lower lip downward toward the chin. Spread of anterior tongue is determined by first eliciting a rooting reflex, just before cupping, by tickling the upper and lower lips and looking for even thinning of the anterior tongue. Cupping is a measure of the degree to which the tongue hugs the finger as the infant sucks on it. Peristalsis is a backward, wave-like motion of the tongue during sucking that should originate at the tip of the tongue and is felt with the back of the examiner?s finger. Snapback is heard as a clucking sound when the tethered tongue loses it grasp on the finger or breast when the infant tries to generate negative pressure. Values are assigned as indicated on the score sheet.
Interpretation of the Hazelbaker Score
- Perfect item score - 2 points
- Perfect Appearance - 10 points
- Perfect Function - 14 points
- Function outweighs appearance
- Function < 11 suggests impaired tongue function
- Appearance < 8 in the presence of impaired function suggests need for frenotomy
Score Sheet for the Hazelbaker Score
Lingual Appearance
| Score | ||||
| Appearance Items | 0 | 1 | 2 |
Hazelbaker Score |
| Appearance of tongue when lifted | Heart- or V-shaped | Slight cleft in tip apparent | Round or square | |
| Elasticity of frenulum | Little or no elasticity | Moderately elastic | Very elastic | |
| Length of lingual frenulum when mid-mouth only with jaw closure tongue lifted | <1 cm | 1 cm | >1 cm | |
| Attachment of lingual frenulum to tongue | Notched tip | At tip | Posterior to tip | |
|
Attachment of lingual frenulum to inferior alveolar ridge |
Attached at ridge | Attached just below ridge | Attached to floor of mouth or well below ridge | |
| Total | ||||
Lingual Function
| Score | ||||
| Function Items | 0 | 1 | 2 |
Hazelbaker Score |
| Lateralization | None |
Body of tongue but
not tongue tip |
Complete | |
| Lift of tongue |
Tip stays at lower alveolar
ridge or rises to |
Only edges to mid-mouth | Tip to mid-mouth | |
| Extention of tongue | Neither of the above, or anterior or mid-tongue humps | Tip over lower gum only | Tip over lower lip | |
| Spread of anterior tongue | Little or none | Moderate or partial | Complete | |
| Cupping | Poor or no cup | Side edges only, moderate cup | Entire edge, firm cup | |
| Peristalsis | None or reverse motion | Partial, originating posterior to tip | Complete, anterior to posterior | |
| Snapback | Frequent or with each suck | Periodic | None | |
| Total | ||||